Ocarina Fingering Chart 8 & 12 Holes
Interactive fingering demonstration + beginner learning guide + free PDF download
Interactive Ocarina Fingering Chart
🎵 How to Use This Interactive Chart
Step 1: Choose Key Signature
Select your desired key signature from the dropdown menu. This will show you which notes are sharp or flat in that key.
Step 2: Click on a Note
Click any note button below to see the correct hole fingering. The ocarina diagram will highlight the holes you need to cover.
Step 3: Learn the Fingering
Study the highlighted holes on the ocarina and read the fingering description. Practice until it becomes automatic!
Select a Note
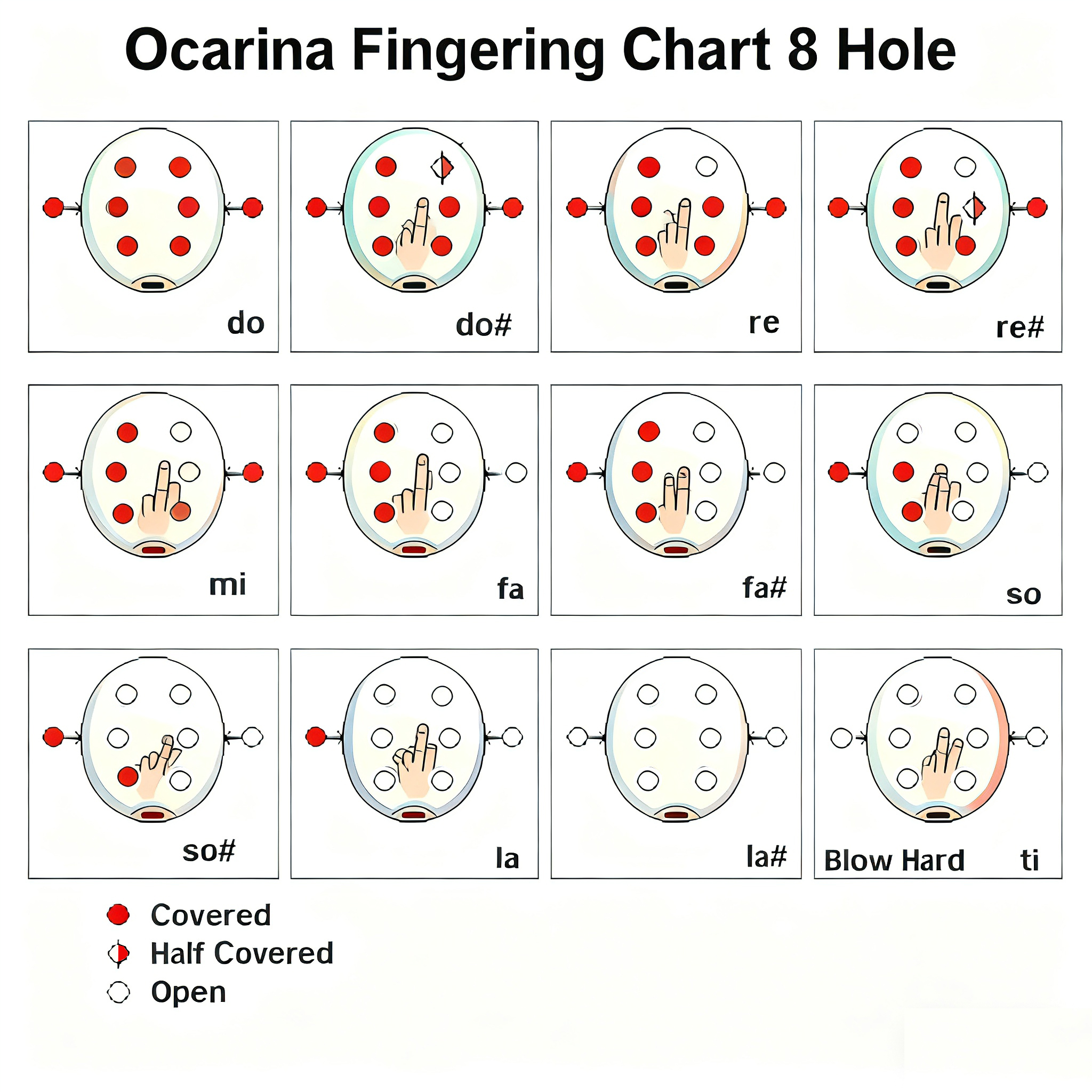
Ocarina Fingering Chart 8 Holes Image
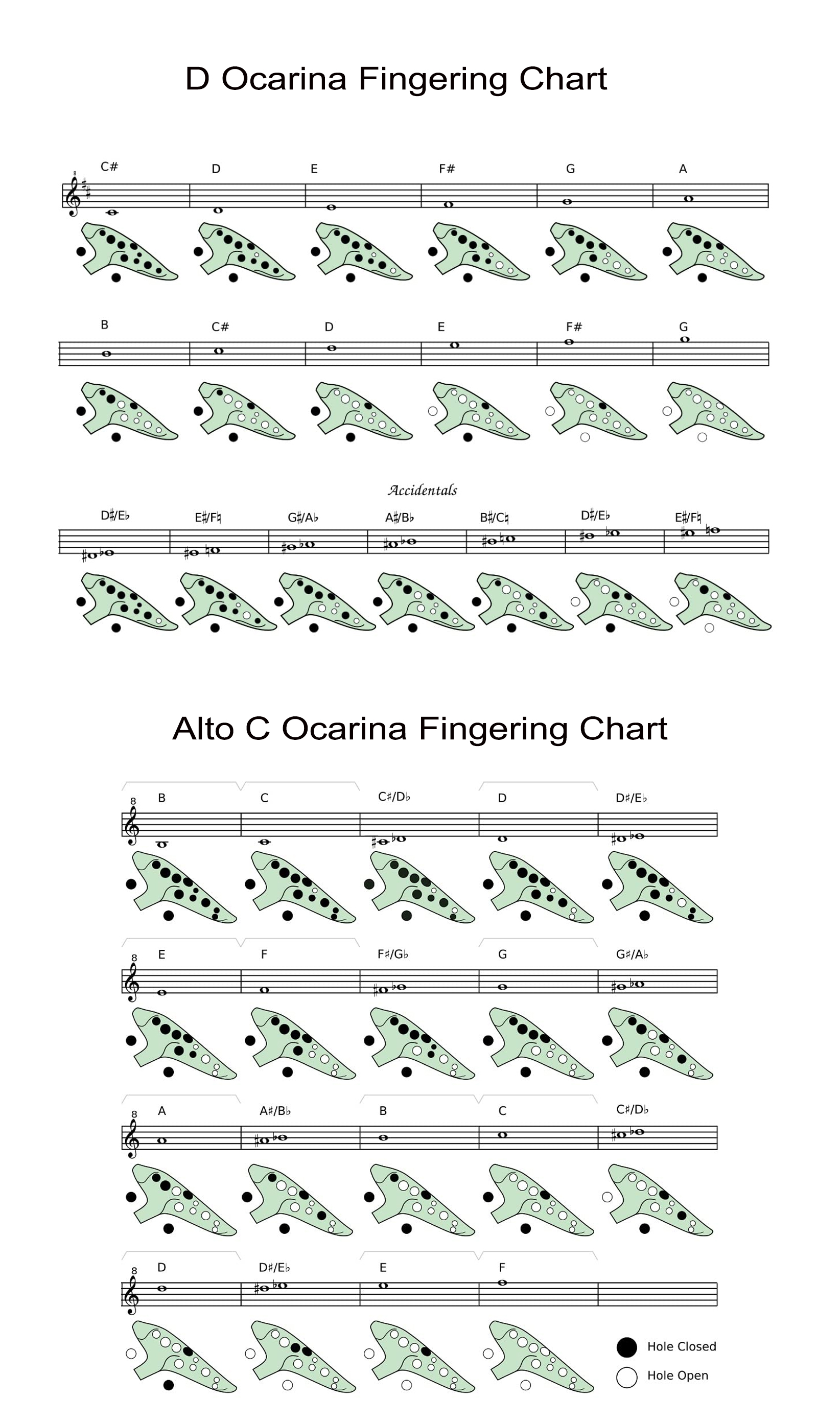
Ocarina Fingering Chart Image 12 Holes(PRINTABLE)
High-quality color PDF perfect for printing and carrying with you. Go to Download Page or open PDF directly: Open PDF
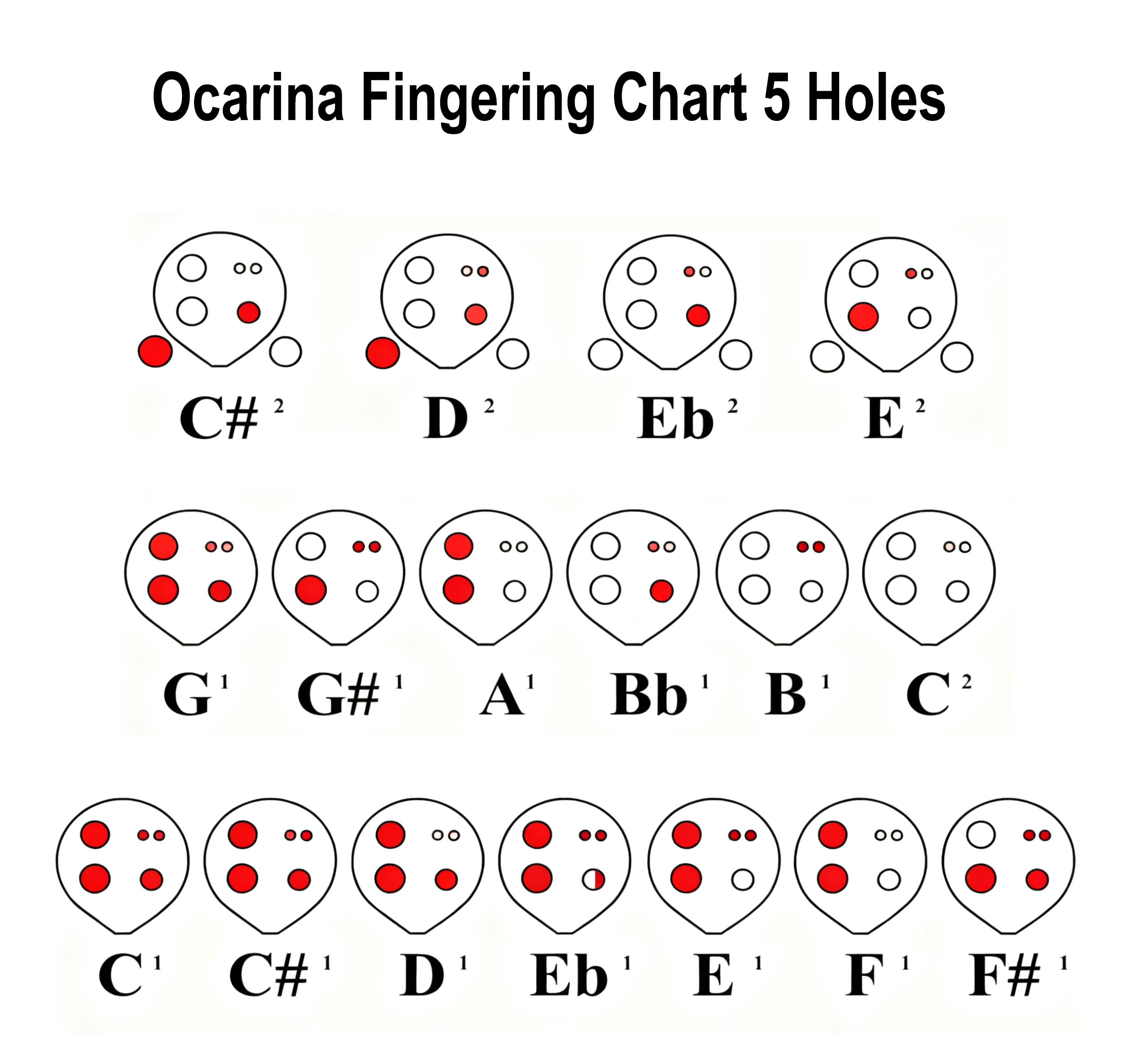
Ocarina Fingering Chart 5 Holes Image
BEGINNER OCARINA FINGERING CHART
(12-Hole Ocarina | Standard C Ocarina)
1. Basic Fingering Combinations
| Note | Hole Pattern | Description |
|---|---|---|
| C5 | ●●●●●●●●●●●● | All 12 holes covered (lowest note) |
| D5 | ●●●●●●●●●●●○ | Hole 12 open |
| E5 | ●●●●●●●●●●○○ | Holes 11,12 open |
| F5 | ●●●●●●●●●○○○ | Holes 10,11,12 open |
| G5 | ●●●●●●●●○○○○ | Holes 9,10,11,12 open |
| A5 | ●●●●●●●○○○○○ | Holes 8,9,10,11,12 open |
| B5 | ●●●●●●○○○○○○ | Holes 7,8,9,10,11,12 open |
| C6 | ●●●●●○○○○○○○ | Holes 6,7,8,9,10,11,12 open (octave) |
Tip: Remember - more holes covered = lower pitch. Cover holes completely with fingertips for clear sound.
2. Essential Beginner Scales
Practice these scales to develop finger dexterity and smooth transitions.
C Major Scale
C5 (all covered) - D5 (12 open) - E5 (11,12 open) - F5 (10,11,12 open) - G5 (9,10,11,12 open) - A5 (8,9,10,11,12 open) - B5 (7,8,9,10,11,12 open) - C6 (6,7,8,9,10,11,12 open)
G Major Scale
G5 - A5 - B5 - C6 - D6 - E6 - F#6 - G6
F Major Scale
F5 - G5 - A5 - Bb5 - C6 - D6 - E6 - F6
3. Simple Practice Melodies
(Great for applying new fingerings!)
"Twinkle Twinkle Little Star":
C5 - C5 - G5 - G5 - A5 - A5 - G5
F5 - F5 - E5 - E5 - D5 - D5 - C5
"Mary Had a Little Lamb":
E5 - D5 - C5 - D5 - E5 - E5 - E5
D5 - D5 - D5
E5 - G5 - G5
"Hot Cross Buns":
B5 - A5 - G5
B5 - A5 - G5
G5 - G5 - G5 - G5
A5 - A5 - A5 - A5
B5 - A5 - G5
4. Ocarina Fingering Tips for Beginners
- Cover holes completely with your fingertips - any air leak will affect the sound.
- Hold the ocarina with both hands, keeping your posture relaxed and comfortable.
- Use steady, controlled breath - don't blow too hard or too soft.
- Start with the middle register (C5-G5) before exploring higher or lower notes.
- Practice one note at a time, ensuring each note sounds clear before moving on.
- Use a mirror to check your finger position and hole coverage.
- Keep your fingers curved and close to the holes for quick transitions.
- Practice scales slowly with a metronome to develop consistent timing.
- Listen carefully to your intonation - use a tuner if available.
- Clean your ocarina regularly, especially the mouthpiece and holes.
- Be patient - mastering hole coverage and breath control takes time.
- Experiment with different air pressures to find the sweet spot for each note.
5-Hole vs. 8-Hole vs. 12-Hole Ocarina Fingering Charts
The core differences between these three ocarina types lie in range breadth, fingering logic, and use cases. Below is a detailed comparison and selection guide tailored to natural American English.
Core Comparison Chart
| Feature | 5-Hole Ocarina | 8-Hole Ocarina | 12-Hole Ocarina |
|---|---|---|---|
| Range | ~8–9 diatonic notes; limited chromatic capability | ~10–11 notes; primarily sequential fingering; limited chromatic range | ~13–15 notes (including chromatics); full 12-tone equal temperament coverage |
| Fingering | Mostly cross-fingering; requires memorizing combinations; partial reliance on breath control | Sequential fingering (scales align with hole order); intuitive to learn | Sequential core scales; chromatics via cross-fingering or split holes; mature, standardized system |
| Use Cases | Kids’ introduction, simple folk music, traditional style performances | Adult beginners, educational settings, basic melody practice | Advanced playing, complex repertoire, professional performances, ensemble/recording work |
| Hole Layout | Typically 5 front holes + 2 rear thumb holes; compact design | Symmetrical 4 front + 4 rear holes; comfortable grip, ideal for smaller hands | 8 main front holes + 2 rear thumb holes + 2 auxiliary holes; some models feature split holes |
Detailed Explanations
5-Hole Ocarina
- Range & Chromatics: Narrowest range—only diatonic scales are feasible, with poor chromatic note access. Limits repertoire choices significantly.
- Fingering Traits: Relies on cross-fingering and breath variation. Easy to pick up initially but hard to advance with; great for quick experimentation or niche traditional styles.
- Typical Uses: Children’s music education, traditional folk performances, portable casual play.
8-Hole Ocarina
- Range & Chromatics: Medium range with intuitive sequential fingering (scales map directly to hole order). Chromatic notes still require special fingerings, making full 12-tone coverage difficult.
- Fingering Traits: Symmetrical hole placement reduces memory load—perfect for adult beginners with no prior musical experience.
- Typical Uses: Teaching tools, amateur playing, foundational melody practice.
12-Hole Ocarina
- Range & Chromatics: Widest range with complete chromatic capability. Ideal for complex melodies and key changes; the standard professional choice today.
- Fingering Traits: Core scales use sequential fingering, while chromatics employ cross-fingering or split holes. The system is well-established, with a gentle learning curve but requires mastering more fingering variations.
- Typical Uses: Professional performances, studio recordings, ensemble work, advanced music instruction.
Buying Guide
- Beginners: Start with an 8-hole ocarina—its sequential fingering builds foundational skills easily. Opt for a 5-hole model only if portability or traditional folk styles are your priority.
- Intermediate Players: Skip the 8-hole and go straight for a 12-hole ocarina. Its range and chromatic capability support long-term growth, eliminating the need to upgrade later.
- Professional Musicians: 12-hole ocarinas are industry standard. High-end models often include split holes or auxiliary holes for enhanced chromatic accuracy and extended range.
Understanding Ocarina Fingerings
Ocarina Anatomy and Parts
Before learning fingerings, it's essential to understand the ocarina's unique vessel flute construction and how it produces its distinctive sweet, mellow sound.
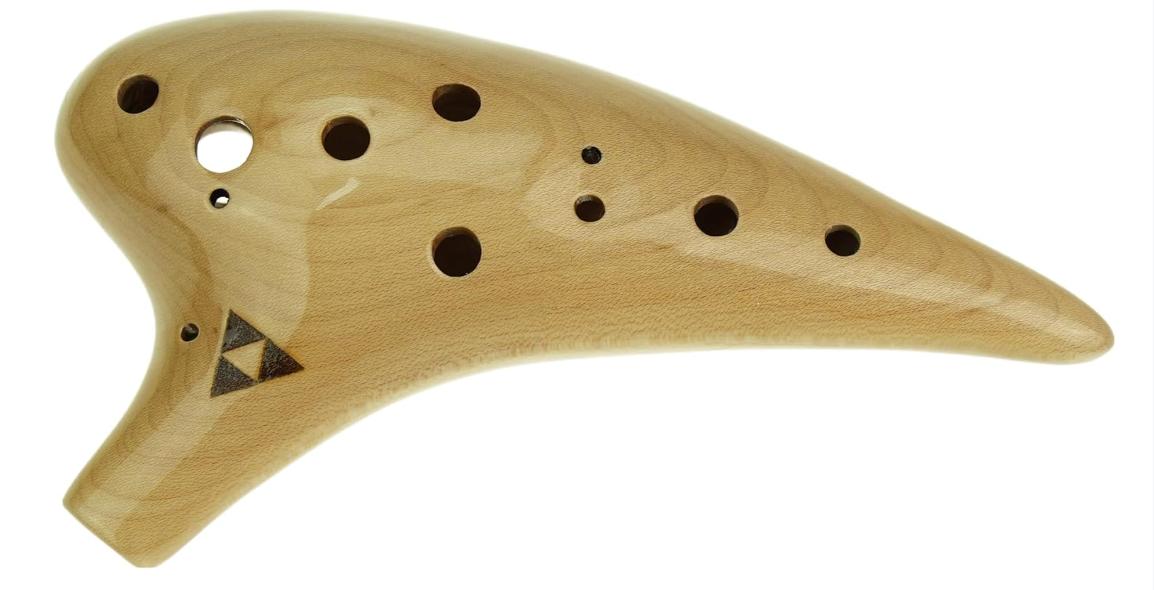

Key Components:
- Body: Hollow vessel made of clay, ceramic, or plastic
- Mouthpiece: Small opening where you blow to create sound
- Finger holes: 4-12 holes that are covered to change pitch
- Material: Traditionally made from clay or ceramic
- Shape: Oval or egg-shaped vessel with a flat bottom
- Chamber: Single air chamber that resonates to produce sound
How Finger Holes Change Ocarina Pitch
The ocarina has multiple finger holes that change the effective length of the air column to alter pitch. When you cover holes, you make the instrument longer and lower the pitch. The ocarina works on the principle of Helmholtz resonance, where the air chamber vibrates at specific frequencies.
Hole Functions:
- Holes 1-4: Covered by left hand fingers
- Holes 5-8: Covered by right hand fingers
- Holes 9-12: Additional holes for chromatic notes
- Subholes: Small holes for half-step variations
Understanding Musical Notes
Musical notes are organized in a specific pattern. Understanding this pattern is crucial for reading music and learning fingerings.
Want a deeper primer? Read our Music Notes Guide for beginners.

The Musical Alphabet:
Musical notes use the letters A, B, C, D, E, F, G, then repeat. In ocarina music, the lowest note is typically C5.
- Natural Notes: C, D, E, F, G, A, B
- Sharp (♯): Raises a note by one half step (e.g., C♯)
- Flat (♭): Lowers a note by one half step (e.g., B♭)
Note: The ocarina is typically pitched in C, meaning when you play "C", it sounds as C on piano.
Half Steps and Whole Steps
Understanding the distance between notes is essential for learning scales and fingering patterns.
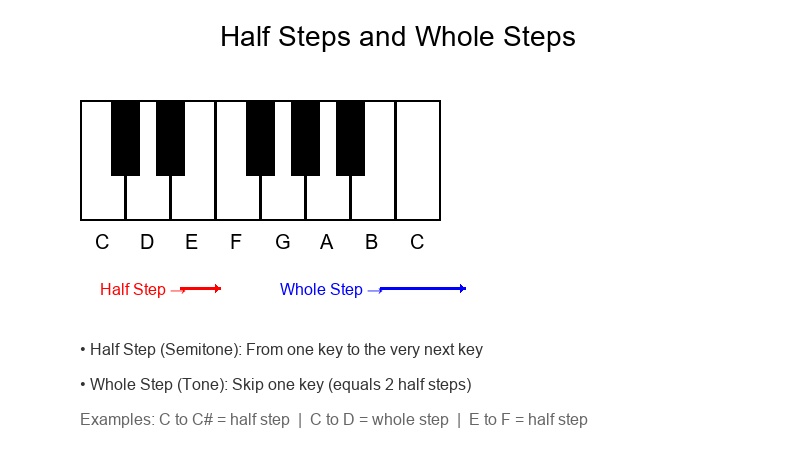
Half Step (Semitone):
The smallest distance between two notes. On a piano, it's from one key to the very next key (including black keys).
Examples:
- C to C♯ (or D♭)
- E to F
- B to C
Whole Step (Tone):
Equal to two half steps. Skip one key on the piano.
Examples:
- C to D (2 half steps)
- F to G (2 half steps)
- A to B (2 half steps)
Ocarina Octaves and Pitch Ranges
An octave is the interval between one note and another with the same letter name but different pitch. The ocarina typically covers about 1.5 octaves.
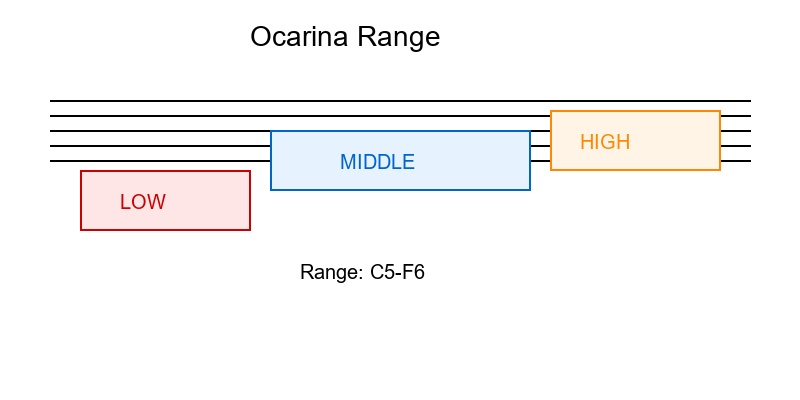
Ocarina Range:
- Low Register: C5 to G5 (fundamental notes)
- Middle Register: A5 to C6 (most comfortable for beginners)
- High Register: C♯6 to F6 (requires advanced technique)
Octave Example: C5 to C6 is one octave. Same fingering, different air pressure and embouchure.
Common Ocarina Fingering Combinations Chart
Here are the most frequently used ocarina fingering combinations. The same fingering can produce different notes depending on your air pressure and embouchure.
| Note | Fingering | Hole Pattern | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C (C5) | ●●●●●●●●●●●● | All holes covered | Lowest note |
| D (D5) | ●●●●●●●●●●●○ | Hole 12 open | One whole step up from C |
| E (E5) | ●●●●●●●●●●○○ | Holes 11,12 open | Major third from C |
| F (F5) | ●●●●●●●●●○○○ | Holes 10,11,12 open | Perfect fourth from C |
| G (G5) | ●●●●●●●●○○○○ | Holes 9,10,11,12 open | Perfect fifth from C |
| A (A5) | ●●●●●●●○○○○○ | Holes 8,9,10,11,12 open | Major sixth from C |
| B (B5) | ●●●●●●○○○○○○ | Holes 7,8,9,10,11,12 open | Major seventh from C |
| C (C6) | ●●●●●○○○○○○○ | Holes 6,7,8,9,10,11,12 open | One octave above C5 |
Tip: Notice how the fingering pattern follows a logical sequence - opening holes from right to left raises the pitch!
Helmholtz Resonance on Ocarina
The ocarina produces notes based on Helmholtz resonance. The air chamber vibrates at specific frequencies determined by the volume of air and the size of the opening (mouthpiece and finger holes).
The resonance frequency depends on:
- Chamber volume: Larger chambers produce lower frequencies
- Opening size: Larger openings raise the pitch
- Air pressure: Higher pressure can produce overtones
- Material: Different materials affect resonance quality
Each fingering pattern creates a different effective opening size, giving the ocarina its full range of notes.
How to Hold the Ocarina Correctly
Left hand: covers holes 1-4 (top holes) with thumb, index, middle, and ring fingers. Right hand: covers holes 5-8 (bottom holes) with thumb, index, middle, and ring fingers. Additional holes 9-12 are covered by the right hand pinky and extended fingers. Hold the ocarina with both hands supporting the instrument, keeping your posture relaxed and comfortable.

How to Learn to Play the Ocarina
- Start with basic notes: establish steady breath support and embouchure, focus on middle register (C5-G5).
- Practice fingerings: use the interactive chart above to click through fingerings while practicing sound production.
- Scale practice: work on C major and G major scales to reinforce fingerings and improve intonation.
- Keep fingering chart handy: reference during lessons and practice to avoid developing bad habits.
- Practice simple melodies: like "Twinkle Twinkle Little Star" and "Mary Had a Little Lamb" to improve musical flow.
- Expand range: gradually explore higher and lower notes while maintaining relaxation.
- Use interactive tools: utilize this page's interactive chart or other fingering simulators for practice.
Best Beginner Ocarina Brands and Models
High-value beginner options: STL Ocarina, Focalink, Night by Noble, Noble. Before purchasing, check build quality, hole alignment, intonation, and warranty. We recommend trying instruments in person with guidance from a teacher or professional.
Practice Tips and Common Mistakes
- Incorrect hole coverage: ensure holes are completely covered with fingertips, avoid air leaks.
- Too much or too little air pressure: aim for steady, controlled air stream, avoid forcing sound.
- Lack of practice structure: set weekly goals (scales, pieces, long tones) and track progress.