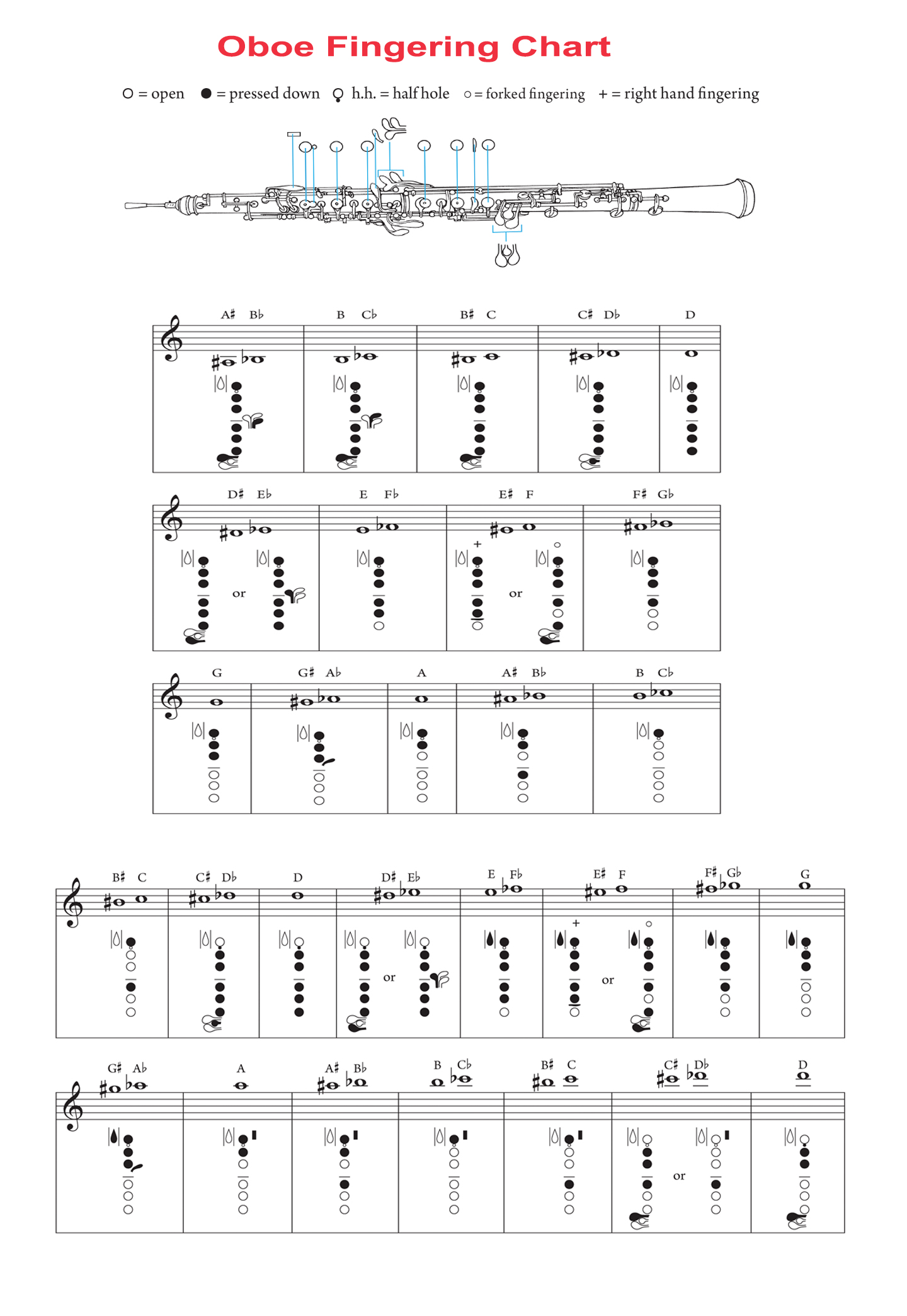
Oboe Fingering Chart
Comprehensive fingering guide + technique tips + beginner learning resources + free PDF download
Interactive Oboe Fingering Chart
🎵 How to Use This Interactive Chart
Step 1: Choose Key Signature
Select your desired key signature from the dropdown menu. This will show you which notes are sharp or flat in that key.
Step 2: Click on a Note
Click any note button below to see the correct key fingering. The oboe diagram will highlight the keys you need to press.
Step 3: Learn the Fingering
Study the highlighted keys on the oboe and read the fingering description. Practice until it becomes automatic!
Select a Note
Oboe Fingering Chart Image (PRINTABLE)
High-quality fingering chart perfect for practice and reference. For a comprehensive guide covering every note from low B♭ to high A with detailed explanations, visit our Complete Oboe Fingering Guide.
BEGINNER OBOE FINGERING CHART
(Standard Oboe | B♭3-A6 Range | Double Reed Instrument)
1. Basic Fingerings & Note Chart
| Note | Left Hand | Right Hand | Thumb Keys | Fingering Description | Octave |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B♭ | 1, 2, 3, 4 | 1, 2, 3, 4 | T1, T2 | All fingers + both thumb keys | B♭3 |
| B | 1, 2, 3, 4 | 1, 2, 3, 4 | T1 | All fingers + left thumb key | B3, B4 |
| C | 1, 2, 3, 4 | 1, 2, 3, 4 | — | All fingers down | C4, C5 |
| D | 1, 2, 3, 4 | 1, 2, 3 | — | All left + first 3 right fingers | D4, D5 |
| E | 1, 2, 3, 4 | 1, 2 | — | All left + first 2 right fingers | E4, E5 |
| F | 1, 2, 3, 4 | 1 | — | All left + first right finger | F4, F5 |
| G | 1, 2, 3, 4 | — | — | All left fingers only | G4, G5 |
| A | 1, 2, 3 | — | — | First 3 left fingers | A4, A5, A6 |
| B | 1, 2 | — | — | First 2 left fingers | B4 |
| C | 1 | — | — | First left finger only | C5 |
| C♯/D♭ | 1, 2, 3, 4 | 1, 2, 3 | T1 | All left + first 3 right + thumb | C♯4, C♯5 |
| E♭ | 1, 2, 3, 4 | 1, 2 | T1 | All left + first 2 right + thumb | E♭4, E♭5 |
| F♯/G♭ | 1, 2, 3, 4 | 1 | T1 | All left + first right + thumb | F♯4, F♯5 |
Tip: Left hand fingers: 1=index, 2=middle, 3=ring, 4=pinky. Right hand fingers: 1=index, 2=middle, 3=ring, 4=pinky. Thumb keys: T1=left thumb, T2=right thumb. Cover tone holes completely for clear sound. Use steady, supported air from diaphragm.
2. Essential Beginner Scales
(Practice these scales daily to build finger dexterity and muscle memory. Focus on smooth transitions and even tone.)
C Major Scale
C (All fingers) → D (All left + R1,2,3) → E (All left + R1,2) → F (All left + R1) → G (All left) → A (L1,2,3) → B (L1,2) → C (L1)
(No sharps or flats - Start with C4)
G Major Scale
G (All left) → A (L1,2,3) → B (L1,2) → C (L1) → D (All left + R1,2,3) → E (All left + R1,2) → F♯ (All left + R1 + T1) → G (All left)
(One sharp: F♯)
F Major Scale
F (All left + R1) → G (All left) → A (L1,2,3) → B♭ (All fingers + T1,T2) → C (All fingers) → D (All left + R1,2,3) → E (All left + R1,2) → F (All left + R1)
(One flat: B♭)
D Major Scale
D (All left + R1,2,3) → E (All left + R1,2) → F♯ (All left + R1 + T1) → G (All left) → A (L1,2,3) → B (L1,2) → C♯ (All left + R1,2,3 + T1) → D (All left + R1,2,3)
(Two sharps: F♯, C♯)
B♭ Major Scale
B♭ (All fingers + T1,T2) → C (All fingers) → D (All left + R1,2,3) → E♭ (All left + R1,2 + T1) → F (All left + R1) → G (All left) → A (L1,2,3) → B♭ (All fingers + T1,T2)
(Two flats: B♭, E♭)
3. Simple Practice Melodies
(Great for beginners to practice fingerings and rhythm! Start in comfortable middle register.)
"Hot Cross Buns" (Traditional):
E (All left + R1,2) → D (All left + R1,2,3) → C (All fingers) → E (All left + R1,2) → D (All left + R1,2,3) → C (All fingers) → C C C C → D D D D → E (All left + R1,2) → D (All left + R1,2,3) → C (All fingers)
(Practice slowly, focusing on clean finger transitions and steady air support)
"Mary Had a Little Lamb" (Traditional):
E (All left + R1,2) → D (All left + R1,2,3) → C (All fingers) → D (All left + R1,2,3) → E (All left + R1,2) → E (All left + R1,2) → E (All left + R1,2) → D (All left + R1,2,3) → D (All left + R1,2,3) → D (All left + R1,2,3) → E (All left + R1,2) → G (All left) → G (All left) → E (All left + R1,2) → D (All left + R1,2,3) → C (All fingers)
(Perfect for learning basic fingerings - maintain steady air pressure)
"Twinkle Twinkle Little Star" (Traditional):
C (All fingers) → C (All fingers) → G (All left) → G (All left) → A (L1,2,3) → A (L1,2,3) → G (All left) → F (All left + R1) → F (All left + R1) → E (All left + R1,2) → E (All left + R1,2) → D (All left + R1,2,3) → D (All left + R1,2,3) → C (All fingers)
(Practice with steady rhythm and clear notes - use proper breath support)
4. Fingering Tips for Beginners
- Keep fingers curved and relaxed—press keys gently, not forcefully.
- Cover tone holes completely—incomplete coverage causes air leaks and poor sound.
- Use proper breath support—support air from your diaphragm, not just your chest.
- Form correct embouchure—say "oh" then place reed between lips, corners firm.
- Practice finger transitions slowly at first—focus on accuracy before speed!
- Keep your right thumb on the thumb rest—it supports the oboe's weight.
- Practice scales daily to build muscle memory for common fingerings.
- Use a metronome to maintain steady rhythm while practicing fingerings.
- Soak reeds properly before playing—dry reeds won't respond well.
- Start with medium-soft reeds—harder reeds require more air pressure.
- Keep fingers close to keys—minimize finger movement for faster technique.
- Check intonation frequently—use a tuner to develop good pitch awareness.
- Practice long tones—develop steady, supported sound on each note.
- Don't bite the reed—use steady air pressure, not jaw pressure.
Common Oboe Fingering Patterns Chart
Here are fundamental fingering patterns to get you started. Mastering these will build a solid foundation.
| Note/Pattern | Fingering/Position |
|---|---|
| Low C | All fingers down + low C key |
| D | All fingers except right pinky |
| E | All fingers except right ring finger |
| F | All fingers except right middle finger |
| G | All fingers except right index finger |
| A | All left fingers, right hand open |
| B | First 3 left fingers |
| C | First 2 left fingers |